Code on Wages Explained
The Code on Wages simplifies four older wage related laws into a single unified framework that protects every worker and reduces compliance effort for employers. It ensures fair wages timely payment gender neutral pay and a standard wage definition that impacts payroll contributions and cost structures. This article explains the Wage Code in simple practical language for HR teams preparing for Labour Codes 2025.
Introduction
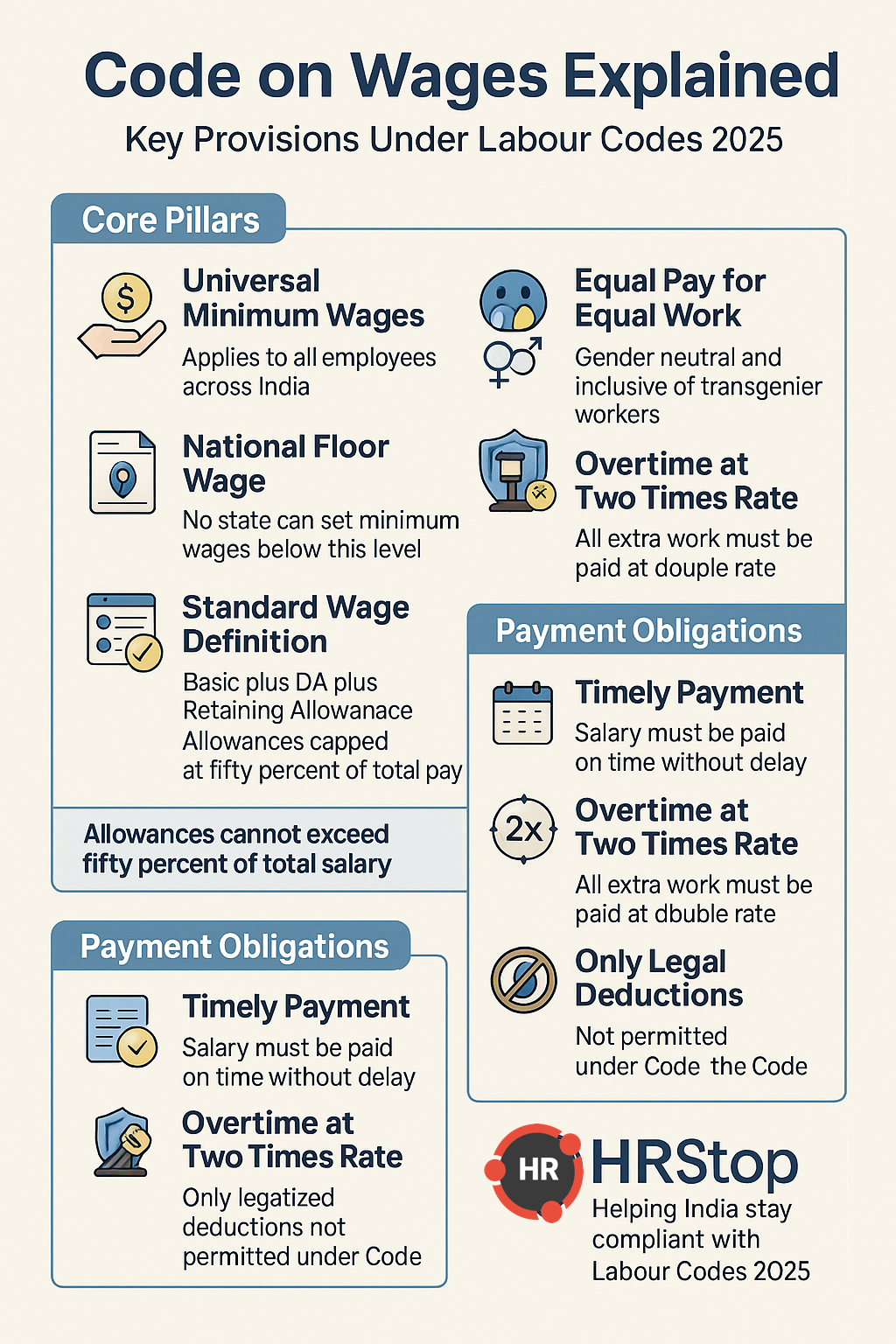
The Code on Wages is one of the most important reforms under the Labour Codes 2025. Earlier wage rules were scattered across multiple laws which created confusion and inconsistency. From November 2025 all wage related matters are governed under a single Code which applies to every employee across every sector and form of employment.
For HR teams this Code changes multiple processes. The Wage Code standardises the meaning of wages introduces the national floor wage ensures universal minimum wages and mandates timely payment without any unauthorised deductions. Equal pay for equal work is now gender neutral and includes transgender workers. Overtime must be paid at twice the normal rate and inspections now follow a digital guidance based approach.
These changes affect payroll calculations job classifications PF ESIC bonus gratuity salary structuring and wage payment cycles. The sections below offer a clear and practical breakdown so your organisation can stay fully compliant with Labour Codes 2025.
Key Changes at a Glance
- Minimum wages apply to every employee
- National floor wage introduced
- Standard definition of wages across India
- Equal pay for equal work across all genders
- Overtime must be paid at twice the normal rate
- Mandatory timely wage payments
- Only authorised deductions permitted
- Online inspections under Inspector cum Facilitator
- Monetary penalties instead of criminal penalties for minor cases
Detailed Explanation of the Wage Code
1. Universal Minimum Wages for All Workers
Earlier only scheduled employments were covered under minimum wages which excluded a large part of India’s workforce. Under the Wage Code every employee must receive statutory minimum wages which ensures a more equal and fair wage system.
What HR Needs to Do
- Classify job roles correctly into skill categories
- Track state wise minimum wage updates
- Review salary structures for full compliance
2. National Floor Wage
The central government will notify a national floor wage based on living standards. No state can set its minimum wage below this amount.
Why This Matters
This brings consistency across India especially for organisations with employees in multiple states.
3. Uniform Definition of Wages
The new wage definition affects PF ESIC gratuity bonus and payroll.
Wages now include Basic plus Dearness Allowance plus Retaining Allowance.
If allowances exceed half of the total salary the excess must be added back to wages.
This prevents artificially low wage components and ensures fair benefit calculations.
For a detailed explanation on how to structure salaries read New Wage Structure and the Fifty Percent Rule
4. Equal Pay for Equal Work
The Wage Code merges earlier equal pay regulations and applies gender neutral protection including transgender workers. Employers cannot differentiate wages recruitment or employment conditions based on gender.
5. Overtime and Payment Timelines
- Overtime must be paid at twice the normal wage rate
- Wages must be paid on time without delays
- Only legally permitted deductions are allowed
These rules strengthen wage fairness and timely financial access for workers.
6. Digital Compliance Through Inspector cum Facilitator
Inspections are now digital and aim to guide employers rather than penalise them. This promotes transparency reduces harassment and brings predictability to wage compliance.
HR Checklist for Immediate Action
HR Checklist for Wage Code Compliance
- Update salary structures using the new wage definition
- Ensure minimum wages are met for every employee in every location
- Configure overtime calculations at twice the normal rate
- Remove any deduction not authorised by law
- Update job descriptions and skill levels
- Train HR and managers on equal pay requirements
- Audit wage payment timelines
- Maintain digital records registers and payslips
Explore HRStop Today
HRStop makes Wage Code compliance easy by automating payroll changes providing state wise minimum wage data generating digital registers and configuring overtime rules. With HRStop your organisation can transition smoothly into Labour Codes 2025.
How HRStop Helps
- Automatic calculations based on the uniform wage definition
- State wise minimum wage library built in
- Overtime rule configuration at twice the wage rate
- Digital payslips registers and audit trails
- Multi location compliance dashboard
- Alerts for wage notifications and rule updates
Related Articles
- India’s New Labour Codes 2025 Overview
- New Wage Structure and the Fifty Percent Rule
- Social Security Code Explained
- EPF and ESIC Changes Under New Codes
- Working Hours Leave and Overtime Rules
- Single Registration License and Return System
- Impact of Labour Codes on Key Industries
Conclusion
The Code on Wages introduces fairness clarity and consistency into India’s wage system. It ensures universal minimum wages equal pay timely wage payments and standard calculations for payroll and benefits. HR teams play a central role in implementing these changes and the right HR technology simplifies this transition. With HRStop employers can stay prepared and compliant under the Labour Codes 2025.
FAQs
What is the scope of the Wage Code
It applies to every employee across every sector and type of employment.
What is the national floor wage
It is a minimum living standard wage set by the central government which states cannot go below.
How does the wage definition affect payroll
It impacts PF ESIC gratuity bonus and salary structure since wages now include Basic plus DA plus Retaining Allowance.
Is overtime at twice the rate mandatory
Yes every overtime hour must be paid at double the normal rate.
Are all deductions allowed
No only deductions permitted under the Code are allowed.
Does equal pay include transgender workers
Yes the Wage Code offers gender neutral protection that includes transgender employees.
What happens if wages are delayed
Delayed wages can attract penalties and repeated delays cannot be compounded.
Rashmi Agarwal
Tuesday, November 25, 2025
Become part of our team
- Full Stack Developer
- Business Development Executive
- Technical Content Writer
- HR Business Partner
- Customer Happiness Executive
- Marketing Executive
One stop solution for all
Hire to Retire needs
HRStop is a complete Hire to Retire HR platform that accelerates the success of your business processes.
